What Is a Deviated Septum?
A deviated septum refers to the displacement of the nasal septum—the thin wall of cartilage and bone that separates the two nostrils—from the midline. When this structure leans to one side, it can cause significant nasal obstruction, breathing difficulties, chronic sinus infections, snoring, and sleep apnea. While mild deviations are common in the general population, more severe cases often require surgical correction.
What Causes Septal Deviation?
There are three primary causes of nasal septum deviation:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Congenital Deformities | Structural irregularities developed during fetal growth or birth trauma. |
| Traumatic Injuries | Resulting from falls, sports injuries, car accidents, or facial trauma. |
| Age-Related Changes | Natural anatomical changes in nasal bones and cartilage with aging. |
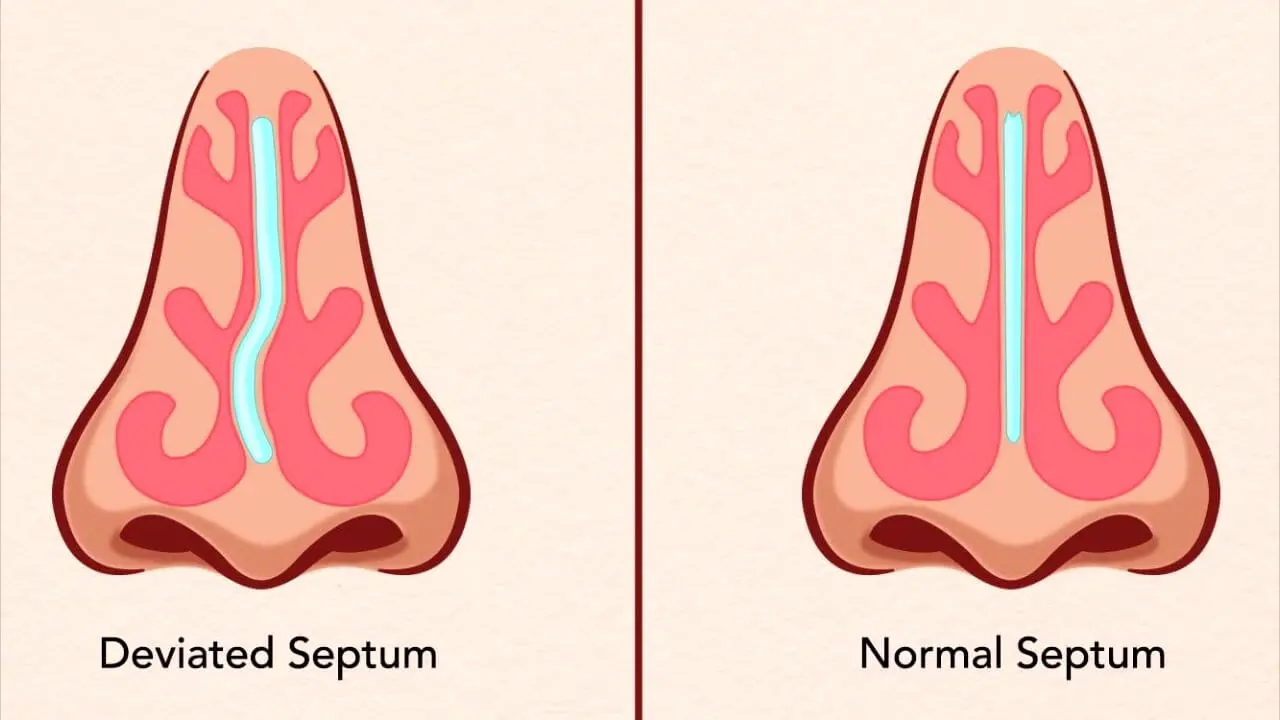
Symptoms of a Deviated Septum
Patients with a deviated nasal septum may experience:
- One-sided or bilateral nasal obstruction
- Chronic mouth breathing and dry mouth
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Postnasal drip and recurrent sinusitis
- Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
- Headaches or facial pressure
- Reduced sense of smell
How Is It Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a detailed ENT (ear, nose, and throat) examination. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Anterior Rhinoscopy: Visual inspection using a nasal speculum
- Nasal Endoscopy: Fiber-optic camera to evaluate deeper nasal structures
- CT Scan: To detect coexisting sinus disease or turbinate hypertrophy
- Rhinomanometry (if necessary): To measure airflow resistance in the nasal cavity
Treatment Options for Deviated Septum
For patients with mild symptoms, temporary symptom control may be achieved using:
- Topical nasal decongestants
- Antihistamines
- Nasal corticosteroid sprays
However, surgical correction through septoplasty remains the only permanent solution.
What Is Septoplasty?
Septoplasty is a functional surgical procedure performed to straighten the deviated septum and improve nasal airflow. The surgery is typically carried out under local or general anesthesia and takes about 30 to 60 minutes.
During the procedure, the surgeon removes or reshapes the deviated portions of cartilage and bone to restore the septum to the midline. When needed, internal nasal structures are repositioned and stabilized.
If the patient also has aesthetic concerns, septoplasty may be combined with cosmetic rhinoplasty, forming a procedure known as septorhinoplasty.
Surgery Overview
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Operation Time | 30–60 minutes |
| Anesthesia | General or local |
| Hospitalization | Outpatient or 1-night stay |
| Recovery Time | Back to daily life in 5–7 days |
| Long-Term Healing | Few weeks to months |
| Success Rate | High with experienced surgeons |
Not: Eğer hastada estetik sorunlar da mevcutsa, bu işlem "septorinoplasti" şeklinde kombine edilebilir.
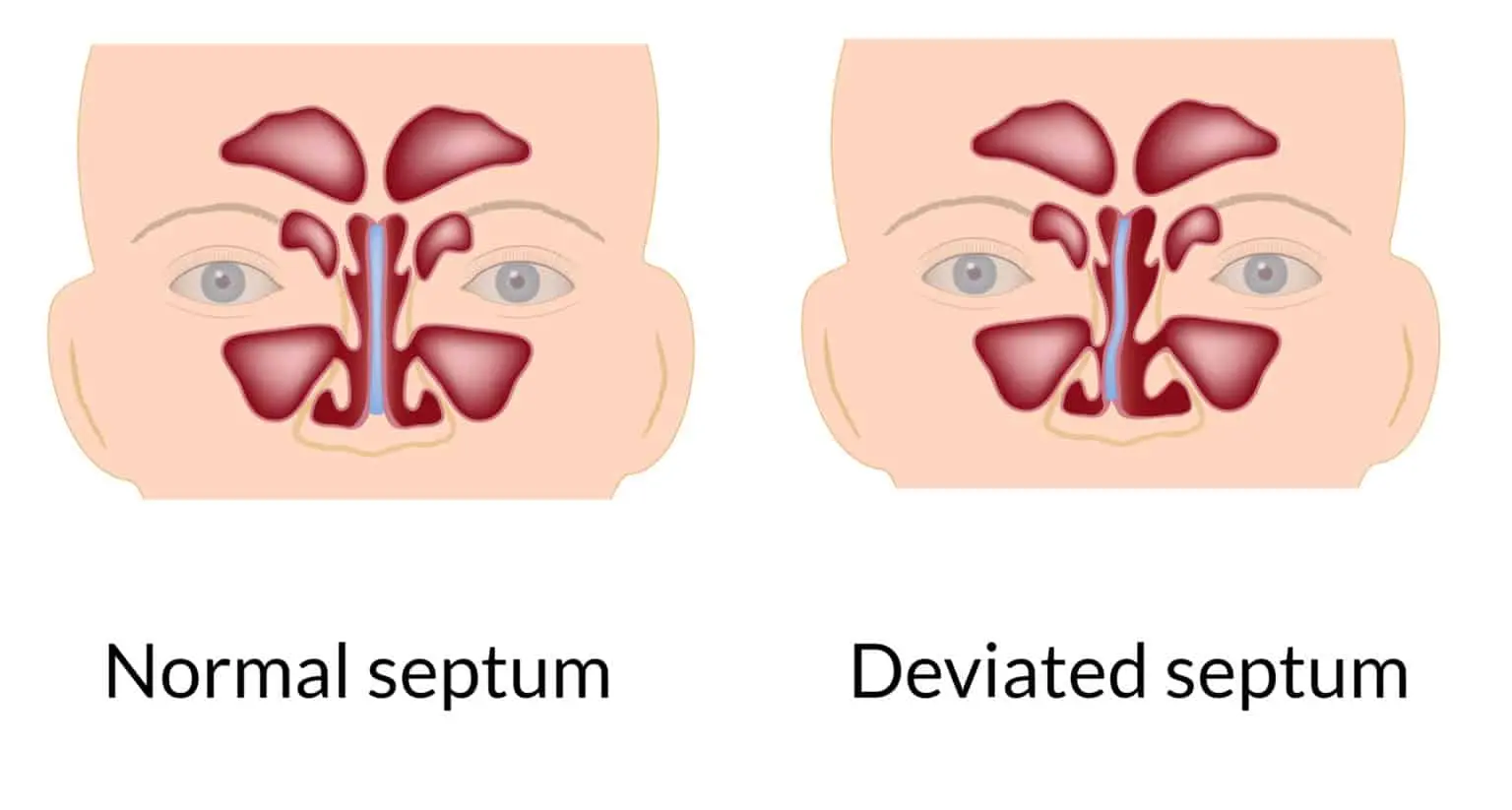
Postoperative Recovery
After the operation:
- Silicone splints may be placed inside the nose to maintain structure and allow airflow
- Mild bleeding and crusting are expected during the first few days
- Most patients return to work and social activities within a week
- Avoid strenuous exercise or nose trauma for 3–4 weeks
Septoplasty Cost in Turkey
The cost of septoplasty in Turkey can vary based on:
- Severity of deviation
- Surgeon’s experience and credentials
- Whether grafts or splints are needed
- Hospital facilities and location
- Type of anesthesia used
In general, patients should expect an affordable price range in Turkey with high-quality care. However, an in-person examination is necessary to determine the exact cost and treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is septoplasty a cosmetic surgery?
No. Septoplasty is a functional procedure aimed at improving breathing. However, if cosmetic changes are desired, it can be combined with rhinoplasty.
Will I have nasal packing after surgery?
Modern septoplasty techniques use silicone splints with airflow channels, which are typically removed within 2–3 days.
Is the surgery painful?
Most patients report mild discomfort, rather than significant pain, after surgery.
Can the deviation come back?
Recurrence is rare but possible—especially due to trauma or abnormal healing.
![dr.leyla-arvas-800×1000.jpg[1] dr.leyla arvas](https://www.quartz.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/dr.leyla-arvas-800x1000.jpg1_.webp)
Author : Op. Dr Leyla ARVAS
Dr Leyla Arvas is an internationally recognised specialist in aesthetic surgery based in Istanbul. Graduated in 1998 from Istanbul University Faculty of Medicine, she has developed her expertise by studying in Taiwan, Japan and Spain during her 20 years of experience.
This article January 28, 2026 was updated on
Editor: admin@quartz.com.tr