What Is a Tonsillectomy?
Tonsils are lymphoid structures located at the back of the oral cavity, one on each side of the throat. As part of the immune system, they serve as the body’s first line of defense against pathogens entering through the respiratory and digestive tracts. However, in some cases, the tonsils may become a frequent source of infection or grow excessively, leading to problems with breathing and swallowing. In such situations, surgical removal of the tonsils — known as tonsillectomy or tonsil surgery — may be necessary.
When Is Tonsillectomy Necessary?
Tonsil removal is not only indicated for frequent infections but also for conditions such as obstructive breathing disorders, abscess formation, and suspicion of tumors. The most common indications for tonsillectomy are:
| Indication | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Recurrent tonsillitis | Surgery is recommended for patients experiencing 5 or more episodes per year. |
| Chronic tonsillitis | Provides a permanent solution for persistent, treatment-resistant infections. |
| Peritonsillar abscess | If abscesses recur, tonsil removal may be required. |
| Obstructive sleep apnea | Enlarged tonsils may obstruct the airway and cause poor sleep quality. |
| Difficulty swallowing | Enlarged tonsils can hinder the passage of food. |
| Unilateral tonsil enlargement | Asymmetrical growth must be evaluated for malignancy. |
Preoperative Evaluation
Prior to surgery, the patient is thoroughly evaluated by an ENT specialist. The assessment may include a physical examination, blood tests, and imaging techniques such as ultrasound or CT scans. In children, sleep apnea screening may be required to determine surgical necessity.
How Is Tonsillectomy Performed?
Tonsillectomy is performed under general anesthesia and through the mouth — no incisions are made on the neck or face. The procedure typically takes 20–30 minutes. Common surgical techniques include:
- Cold steel (traditional dissection method)
- Electrocautery tonsillectomy
- Plasma or radiofrequency tonsil removal
- Laser tonsillectomy (in selected cases)
- Most patients are discharged on the same day, though a short hospital stay may be needed for young children or those with systemic conditions.
Recovery After Tonsil Surgery
During the first week after surgery, patients may experience throat pain, difficulty swallowing, referred ear pain, and low-grade fever — all of which are considered part of the normal healing process. Full recovery usually takes 7–10 days.
Postoperative Care Instructions:
- Drink plenty of fluids for the first 48 hours
- Avoid acidic or hard foods
- Eat soft, lukewarm meals
- Use pain relievers and antibiotics as prescribed
- Avoid physical exertion, hot showers, and anything that may raise blood pressure
Potential Complications
Although tonsillectomy is generally a safe procedure, the following rare complications may occur:
- Primary or secondary bleeding
- Anesthesia-related risks
- Dehydration due to pain-induced reduced fluid intake
- Temporary changes in taste
To minimize risks, the surgery should be performed by experienced ENT surgeons in well-equipped medical facilities.
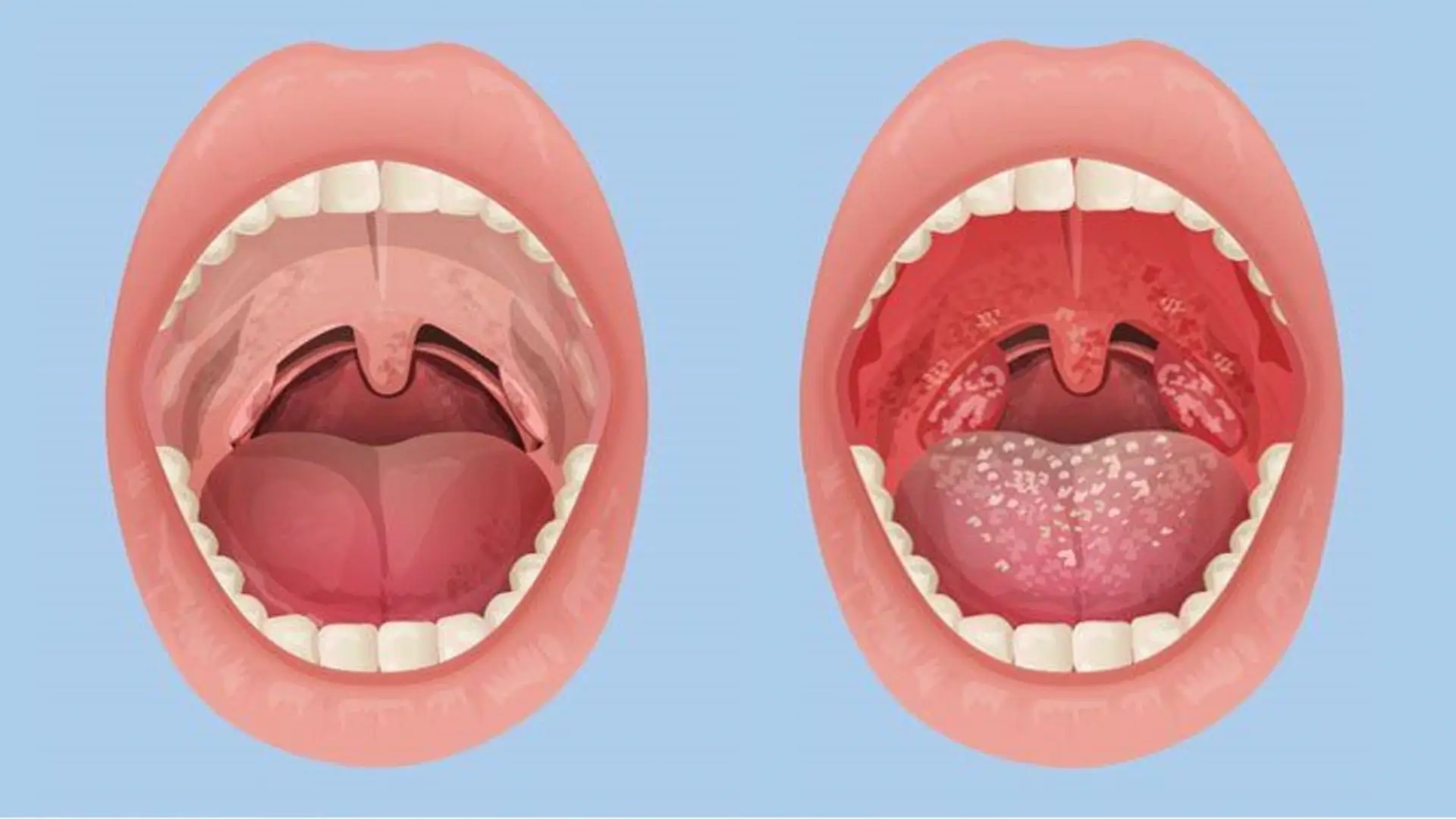
Benefits of Tonsil Removal
- Elimination of frequent tonsil infections
- Reduction or resolution of snoring and sleep apnea
- Improved eating and speech comfort
- Relief from chronic throat irritation and bad breath
Enhanced cognitive and physical development in children through improved sleep quality
Frequently Asked Questions
At what age can tonsillectomy be performed?
It is generally considered safe from age 3 onward, though younger children with severe breathing issues may be eligible earlier.
Can tonsils grow back after removal?
No. Surgically removed tonsil tissue does not regenerate, although rare residual tissue may enlarge slightly.
How long does postoperative pain last?
The most intense pain occurs within the first 3 days and usually improves significantly by day 7–10.
Does removing the tonsils weaken the immune system?
No. After adolescence, tonsils play a reduced role in immunity. Chronically infected tonsils may actually burden the immune system rather than support it.
Tonsillectomy, when performed with the right medical indication, significantly improves quality of life. It is a safe and effective procedure for patients suffering from frequent infections, breathing or swallowing difficulties, or sleep disturbances. Planning the surgery with an experienced ENT specialist and choosing a fully equipped center ensures optimal outcomes and patient satisfaction.
![dr.leyla-arvas-800×1000.jpg[1] dr.leyla arvas](https://www.quartz.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/dr.leyla-arvas-800x1000.jpg1_.webp)
Author : Op. Dr Leyla ARVAS
Dr Leyla Arvas is an internationally recognised specialist in aesthetic surgery based in Istanbul. Graduated in 1998 from Istanbul University Faculty of Medicine, she has developed her expertise by studying in Taiwan, Japan and Spain during her 20 years of experience.
This article January 28, 2026 was updated on
Editor: admin@quartz.com.tr